Growth And Advancements In Transdermal Drug Delivery
By Deboleena Dutta, Research Nester
Transdermal medications can penetrate the epidermis, enter local blood arteries, and then reach the circulatory system due to their low molecular weight (<600 g/mol), addressing a variety of challenges in traditional drug delivery.
By using skin as a portal for medication delivery, transdermal systems provide a competitive edge to pharmaceutical companies in several ways:
- Improved patient compliance: Transdermal patches simplify the drug administration process, making it easier for patients to adhere to their treatment plans, which is particularly beneficial for long-term treatments where daily injections or oral medications may lead to non-compliance. For instance, fentanyl patches are put on and taken off after 72 hours.
- Targeted delivery and controlled release: Transdermal systems precisely control the delivery of drugs, ensuring more consistent therapeutic effects with fewer side effects compared to traditional delivery methods.
- Innovative drug delivery: Pharma giants are investing in transdermal delivery, with Anodyne Nanotech’s HeroPatch achieving high bioavailability for GLP-1 receptor agonists, advancing next-gen drug delivery for complex biologics.
- Cost-effectiveness: Transdermal systems reduce the need for expensive and invasive medical procedures, offering healthcare cost savings in the long term.
In this article, we explore the growth, technologies, and trends shaping the transdermal drug delivery system market, revolutionizing non-invasive drug administration.
Market Overview
The transdermal drug delivery (TDD) system industry is experiencing significant growth, spurred by the increasing demand for non-invasive and patient-friendly alternatives to conventional drug delivery methods. According to Research Nester Analysts, the market for transdermal drug delivery systems was valued at around USD 74.6 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.2% to reach USD 296.9 billion by the end of 2037.
The market is evolving rapidly, driven by several factors, including:
- the rising prevalence of chronic diseases
- the shift toward personalized medicine
- advancements in drug formulations
- rising patient preference for non-invasive treatments
- focus on biologics and peptides
- integration with wearable devices.
Advanced Technologies In Transdermal Drug Delivery
Transdermal drug delivery is benefitting from a range of advanced technologies that enhance drug absorption and enable the delivery of more complex therapeutics. The adoption of these technologies is driving the evolution of TDD systems, making them more effective and versatile in treating a variety of conditions. Here’s a look at how each technology contributes to TDD:
- Electroporation: This technique uses brief high-voltage (50-3000V), short duration (5 μs to 100 ms) pulses to temporarily open skin barriers, enabling non-invasive delivery of large molecules like peptides, proteins, and nucleic acids. This technology is especially valuable for transdermal administration of biologics, which are otherwise challenging to deliver.
- Radio Frequency: This innovative technology significantly enhances transdermal drug delivery systems by improving skin permeability. It enables more efficient and controlled drug absorption, thereby expanding treatment options for various medical conditions, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes and enhanced therapeutic effectiveness.
- Iontophoresis: In this method, a small electrical current is applied to push charged drug molecules into the skin, enhancing the penetration of both small and large molecules. This technique is widely used for delivering drugs such as corticosteroids and local anesthetics, and it's expanding into more complex therapeutic areas.
- Microporation: Microneedle technology enhances transdermal drug delivery by creating micro-channels for controlled drug release, ensuring faster absorption with minimal discomfort. Its growing prominence was highlighted by the FDA’s 2023 approval of ZYNTEGLO, a microneedle patch delivering thioperamide for post-surgery nausea, showcasing its expanding medical applications.
- Mechanical Arrays: This technology uses arrays of microneedles or other mechanical devices to promote drug absorption by creating micro-channels in the skin. The precision and controlled depth of penetration makes it ideal for delivering a range of therapeutics with minimal discomfort, offering a non-invasive alternative to traditional injections.
- Ultrasound: This technology uses high-frequency sound waves to temporarily increase skin permeability. This non-invasive technique enables efficient drug delivery, especially for larger molecules or those requiring more complex transdermal systems. It is gaining traction in dermatology and chronic disease management.
- Thermal: The application of heat significantly improves skin permeability, enhancing drug absorption. Techniques like thermophoresis further optimize drug delivery, enabling more effective and targeted treatments for various health conditions.
Each of these technologies is pushing the boundaries for what is possible with transdermal drug delivery, creating a more efficient, versatile, and patient-friendly treatment landscape. As innovation continues, the potential for TDD will expand, making it an increasingly prominent player in modern healthcare.
Spotlight On Therapeutic Areas
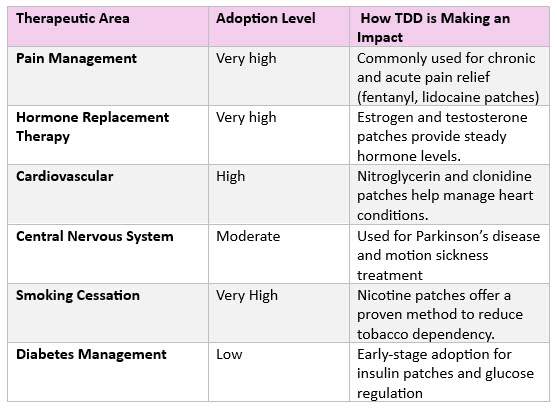
Transdermal drug delivery isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution-; it’s tailored to different medical conditions and drug types. Some therapies require slow, sustained release, while others need rapid absorption. So, where is TDD making the biggest impact? Let’s break it down by therapeutic application:
Global Hotspots for Transdermal Drug Delivery
The transdermal drug delivery industry is thriving worldwide, but growth isn’t uniform across regions. North America dominates, driven by advanced healthcare infrastructure and strong R&D investments. Europe follows closely, with rising demand for non-invasive drug delivery. Meanwhile, Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing region, fueled by expanding healthcare access and an aging population. Latin America and the Middle East & Africa are catching up, as improving medical facilities drives interest in innovative drug delivery solutions.
Looking To The Future
The transdermal drug delivery system is revolutionizing drug administration by offering a seamless blend of efficiency, convenience, and patient comfort. As cutting-edge technologies enhance absorption and expand therapeutic possibilities, pharmaceutical giants are doubling down on investments, recognizing TDD’s vast potential. With a growing emphasis on personalized medicine and sustainable solutions, this market is on the brink of a major transformation. As innovation accelerates, transdermal delivery is set to redefine the future of healthcare, and we need to get ready to embrace its full potential.
 About The Author:
About The Author:
Deboleena Dutta is a junior content writer at Research Nester and is a biotech engineer by profession.
