Nanotechnology Drug Delivery: A Market Overview
By Aashi Mishra, Research Nester

The last decade has seen an evolution in nanotechnology from lab curiosity to a disruptive force in advanced medicine, with the most noticeable influence surfacing in drug delivery. Notably, in 2023, a cancer patient in the U.S. received a nanocarrier-powered chemotherapy formulation that delivered drugs directly to tumor cells, sparing healthy tissue.1 Milestones such as these are moving novel technologies from trials to scheduled care and prompting global investment and commercial interest.
For business leaders, investors, and R&D heads, this shift matters. Nanotech drug delivery is not an academic specialty; it’s a commercial platform reshaping pipelines, shortening time-to-market for complex biologics, and unlocking therapeutic modalities that were previously impractical. According to new market research analysis by Research Nester, the nanotechnology drug delivery industry was valued at $107.65 billion in 2025 and is likely to cross $261.95 billion by 2035, registering more than 9.3% CAGR between 2026 and 2035.
The Practical Promise: Why Delivery Matters More Than Ever
Therapeutic innovation is only as useful as the ability to deliver drugs safely and effectively.
Nanocarriers, lipid nanoparticles (LNPs), polymeric nanoparticles, dendrimers, inorganic nanosystems, and hybrid platforms solve three persistent problems: poor solubility of many small molecules, fragility and immunogenicity of modern biologics (like mRNA and siRNA), and the systemic toxicity of potent agents such as chemotherapeutics. The pandemic accelerated acceptance of LNP technology with the utilization of mRNA vaccines, which reached hundreds of millions of recipients globally; this real-world validation has opened investor and regulatory attention to nanocarriers for vaccines, oncology, rare diseases, and gene therapies.
Emerging Trends Defining The Next Decade
1. Smart & Stimuli-Responsive Nanoparticles
The next generation of healthcare advancements is less about targeting the affected muscles or tissues and more focused on triggered release. Nanoparticles are being designed to release their payload only in response to specific tumor microenvironments, including low pH, or interaction with particular enzymes. Nanocarriers increasingly combine payload delivery with targeting ligands, immune modulators, or imaging agents. This practice, known as Trojan horse strategy, is becoming extremely popular to treat chronic and rare diseases as it targets the affected tissue directly, reducing toxicity. Research on smart materials such as mesoporous silica and intelligent polymers is rapidly advancing this field. These integrated therapies command premium pricing and strong clinical differentiation.
2. Modern Nanoparticle Delivery Strategies
Researchers, healthcare providers, and doctors are continuously finding ways to discover more advanced and potent techniques to treat cancer patients. The breakthrough in nanoparticle sciences, such as LNPs, polymeric nanoparticles, and exosome-based delivery, is creating more protected, personalized, and producible substitutes for delivering CRISPR, siRNA, and mRNA. These scientific advances allow researchers to develop robust genetic medications that can address rare diseases.
3. Multimodal Theranostics
Theranostics is a combination of therapy and diagnostics in a single nanoparticle. A single agent can be imaged in a tumor through MRI or PET contrast, which allows for confirmation the treatment has reached the target, and then, on command, delivery of a therapeutic payload. This allows for real-time treatment monitoring and personalized dosing.
4. Digital Discovery and AI-Driven Design
The combinatorial complexity of nanoparticle design is immense. Artificial intelligence and machine learning are now being used to model nanoparticle behavior in silico, predict biological interactions, and optimize designs before a single experiment is run. This dramatically accelerates the development timeline and reduces costs.
5. Manufacturing and Commercialization Advancements
Advances in microfluidic production, continuous flow reactors, and high-throughput characterization tools are lowering the cost and variability of nanoparticle manufacturing. Investors and buyers value suppliers that can demonstrate scalable, reproducible production under GMP standards. The COVID-19 mRNA vaccines from Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna are, at their core, a nanotech delivery triumph. The overwhelming success of these two mRNA-based vaccines, with around 95% efficacy in Phase 3 clinical trials, can be attributed to their unique LNP nanocarrier and the manufacturing and commercialization efforts to streamline availability.
The Engine Of Growth: Government Backing And Major Pharma Bets
Any revolution requires curiosity, funding, and infrastructure. The nanotechnology industry has seen massive growth because of the support, positive infrastructure, and constant attention from the researchers. Academic and industry labs report steady progress in tumor-targeting nanoparticles, antibody-decorated carriers, and immunomodulatory nanoformulations that improve tumor penetration and reduce off-target effects. These programs have directly accelerated progress in areas such as tumor-targeting nanoparticles, antibody-decorated drug carriers, and immunomodulatory nanoformulations — technologies that improve tumor penetration, enhance drug precision, and significantly reduce off-target toxicity. Government-backed flagship projects have also advanced nanoparticle-enabled diagnostics, nano-based cancer vaccines, and lab-to-clinic translational platforms. Some of the government funding includes:
1. Government Agencies as Catalysts
Government authorities understand the capacity nanomedicine developments hold in treating hard-to-cure diseases and are therefore supporting research through multi-agency, multiyear R&D programs.
Government Investments in Nanotechnology R&D (Top 5 Countries)
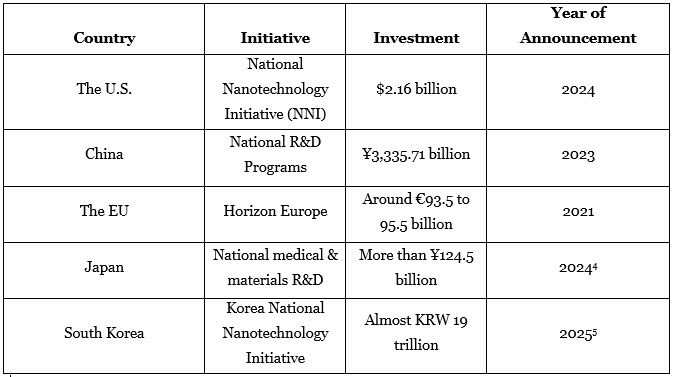
Each country has implemented its own governmental initiatives and investments in nanotechnology.
- The U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH) and National Cancer Institute (NCI) have long-running programs, including the Cancer Nanotechnology Plan. The NIH announced an annual budget of around $48 billion for biomedical research, clinical trials, and infrastructure grants to discover novel systems in fiscal year 2024.6
- Major Asian countries, including China, Japan, South Korea, etc., are focusing on nanocarrier development and investing billions to improve their domestic biopharmaceutical infrastructure. A significant example is India’s allotment of around 3,000 crore to the Department of Health Research to develop novel technologies in healthcare.7
2. Big Pharma's Strategic Pivot: Acquire, Partner, Invest
Major pharmaceutical companies, hungry for differentiated pipelines in the face of patent cliffs, are actively building their nano-delivery arsenals. There are pragmatic commercial reasons investors and Big Pharma are moving decisively to acquire, partner, and invest in nanotech delivery. First, nanotechnology unlocks difficult therapeutic classes that require more sophisticated carriers, such as, for example, nucleic acids, potent cytotoxins, and hydrophobic small molecules. Second, these carrier technologies can carry multiple medications to different targets, which reduces and spreads the cost over multiple R&D projects. These strategies initiated by Big Pharma are often worth hundreds of millions to billions, which validates the technology's value.
AstraZeneca invested more than $2.9 billion to acquire Ionis Pharmaceuticals' cardiology pipeline. The driver of the acquisition was primarily dependent on ligand-conjugated antisense (LICA) technology.8 Novartis also has an ongoing investment in gene therapies delivered via viral vectors and LNPs, funding around EUR 40 million of investments to establish its first specialized viral vector production facility in Europe, more specifically in Slovenia, in February 2025.9
Overall, the most prominent market players in nanotech drug delivery are:
- AbbVie
- Celgene
- Johnson & Johnson
- Nanobiotix
- Nanocarrier
- Merck & Co.
- Novartis International
- Pfizer
- Sanofi
- SkyePharma
- Starpharma Holdings
- Teva Pharmaceutical Industries
Commercial & Clinical Challenges — And Practical Mitigations
No technology is without risk. Nanomedicines face complex CMC requirements, biodistribution uncertainties, and legacy skepticism tied to early-stage toxicity concerns. However, those risks are increasingly tractable: improved physicochemical characterization, better in vitro–in vivo correlation models, and iterative safety testing to reduce unknowns. Partnerships that pair therapeutic experts with delivery experts, and outsourcing to specialized CMOs with nanoparticle GMP capability, are practical mitigations that many program teams employ. For investors, the due diligence checklist should emphasize manufacturing reproducibility, regulatory strategy, and the degree to which a delivery platform is agnostic to payloads.
Final Thought
Government programs and public funding reduce early technical risk; leveraging these can improve program economics and speed translational milestones. As the technology continues to mature, those who combine scientific rigor with disciplined commercialization will be best placed to capture the market’s upside. Nanotech drug delivery is no longer a speculative frontier. It is a growing, regulated, and capitalized industry segment that improves therapeutic performance while creating scalable business models.
References
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/397453320_RECENT_ADVANCES_IN_NANOCARRIERS_FOR_TARGETED_CANCER_THERAPY#:~:text=Abstract%20and%20Figures,delivery%20while%20minimising%20systemic%20toxicity.
- https://www.nano.gov/sites/default/files/pub_resource/NNI-FY24-Budget-Supplement.pdf?utm
- https://www.stats.gov.cn/english/PressRelease/202410/t20241014_1956904.html?utm
- https://www.amed.go.jp/content/000139647.pdf?utm
- https://www.msit.go.kr/eng/bbs/view.do?bbsSeqNo=42&mId=4&nttSeqNo=1033&sCode=eng&utm
- https://www.nih.gov/about-nih/organization/budget?utm
- https://www.indiabudget.gov.in/doc/eb/sbe47.pdf?utm
- https://www.astrazeneca.com/media-centre/press-releases/2021/astrazeneca-ionis-to-collaborate-on-eplontersen.html#!
- https://www.novartis.com/si-en/news/media-releases/slovenia-novartis-opens-its-first-specialized-viral-vector-production-facility-europe
About The Author:
 Aashi Mishra is an experienced research writer, strategist, and marketer at Research Nester. She has a demonstrated history of research in a myriad of industries and distills complex industrial terminologies of market space into simpler terms.
Aashi Mishra is an experienced research writer, strategist, and marketer at Research Nester. She has a demonstrated history of research in a myriad of industries and distills complex industrial terminologies of market space into simpler terms.
